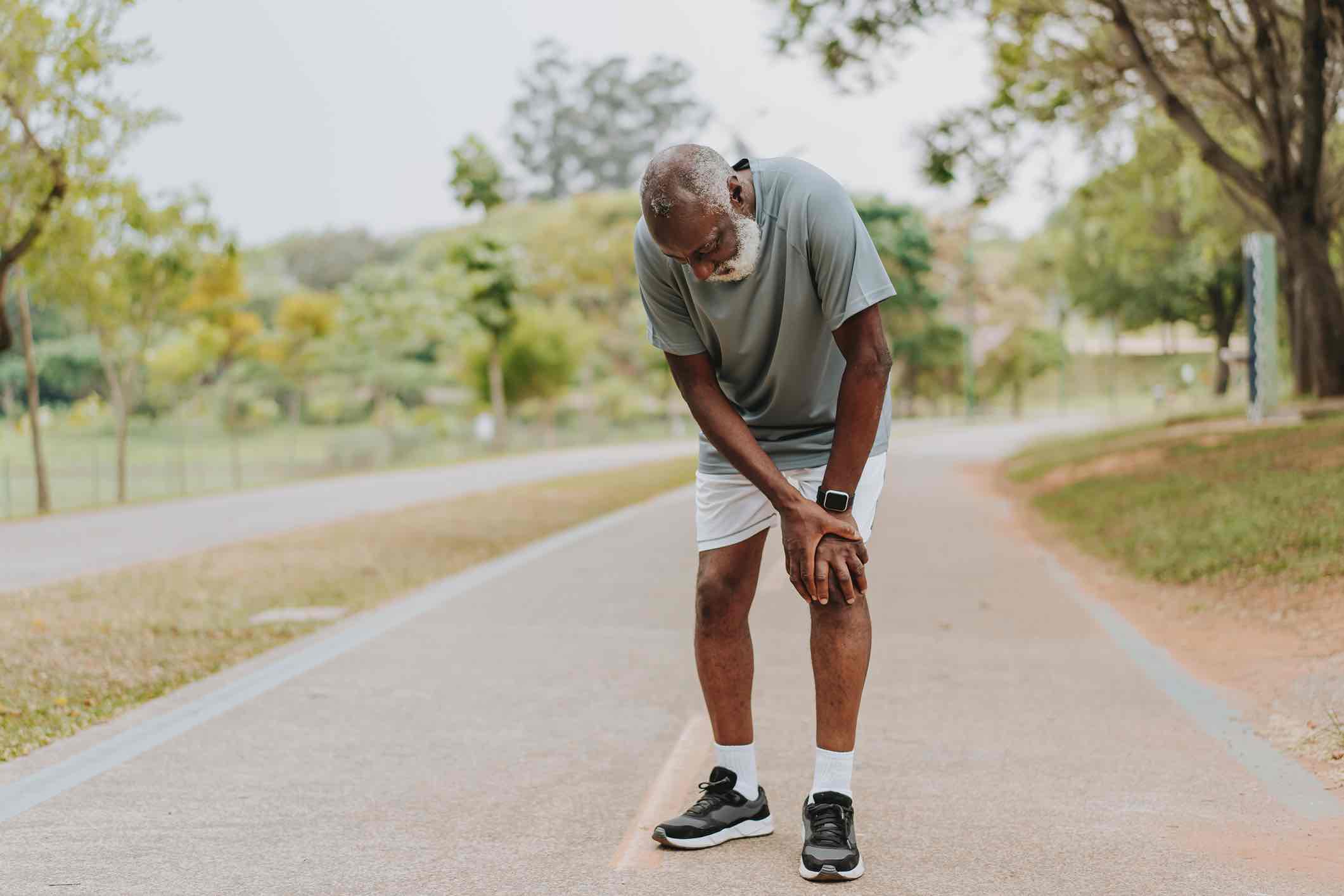
If you live with arthritis pain, you know it can affect you throughout your everyday life—from the simple things like getting dressed in the morning to the more complex things like doing your job well. If you are living in pain and frustration, you are not alone. Arthritis is common—in the United States, over 53 million people have arthritis, and it’s the No. 1 cause of work-related disability. Luckily, there are several arthritis treatments that can help ease pain and increase range of motion for patients. At WMCHealth, our orthopedic specialists are experts in arthritis care and can help you find relief.
What Is Arthritis?
Arthritis occurs when joints become swollen and tender, causing them to feel pain and stiffness. Although there are several types of arthritis, the most common types are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, both of which occur most often in middle-aged and elderly people.
Symptoms of Arthritis
Although symptoms will vary depending on the type of arthritis you have, common ones include:
- Joint pain that doesn’t go away
- Redness
- Warmth
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Limited range of motion
Types of Arthritis
There are many different types of arthritis. Although the condition can affect any joint in the body, it typically affects the hands, wrists, hips, feet, ankles, knees, lower back, and shoulders.
Osteoarthritis
Often described as wear-and-tear arthritis, this is the most common type of arthritis, and it often occurs in patients over age 50. Common joints affected include the knees, hips, and fingers.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
This is an autoimmune, inflammatory form of arthritis that happens when the body attacks the joints. It’s most likely to show up between the ages of 30 and 60, and most commonly involves the small joints of the hands and feet.
Psoriatic Arthritis
This type of autoimmune arthritis occurs in people who also have psoriasis on their skin. It’s most commonly seen between the ages of 30 and 55, and it typically affects the small joints of the hands and feet.
Gout
This condition is most common in middle-aged men, and it often causes very sharp, intense pain in the joints. Gout comes and goes, and while it can involve any joint, it typically impacts the big toe, ankles, knees, wrists, and fingers.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
This disease causes arthritis of the spine, and it typically occurs in young men with back pain. It’s most common in patients between the ages of 17 and 35, and experts believe it has a genetic component.
Juvenile Arthritis
Arthritis that occurs in children under 16 is called juvenile arthritis.
Reactive Arthritis
Reactive arthritis is joint pain that’s triggered by an infection in the body. Common causes of reactive arthritis include urinary tract infections (UTIs) or infections in the intestines.
Arthritis Risk Factors
Although arthritis can affect anyone, females and people over 50 are more at risk. Other common risk factors include:
- Family history
- Tobacco use
- Sedentary (non-active) lifestyle
- Obesity
- Athletes or those with physically demanding jobs
- Other autoimmune conditions
Diagnosing Arthritis
If you suspect you might have arthritis, it’s important to visit your doctor, as there are many treatments that can help ease your symptoms.
Your doctor will first do a physical exam to test how well you can move your joints and to see if they feel swollen, red, or warm. If they suspect you have a form of arthritis, they will likely then order blood, urine, and/or joint fluid tests, which can help determine what type of arthritis you have. They may also order an X-ray, CT scan, ultrasound, or MRI to better understand what’s causing your joint pain.

Treatment for Arthritis
Treatment for arthritis depends both on the type of arthritis and the severity of your symptoms.
- Medication : Some people will benefit from the use of NSAIDs—like ibuprofen and naproxen. Other patients will benefit from counterirritants, which are topical creams and ointments. People with extensive symptoms might need steroid medications (like prednisone) or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), which can be infusions or injections
- Therapy : Physical therapy or occupational therapy can be helpful in the treatment of arthritis.
- Surgery : In severe arthritis cases, your doctor may recommend surgery—such as joint replacement or joint fusion.
Why Choose WMCHealth?
WMCHealth’s Division of Rheumatology has board-certified rheumatologists who can help you figure out what type of arthritis you have, as well as the most effective treatment possible. The Division of Rheumatology works as full-time faculty at New York Medical College, where we train medical students and residents. This commitment to training and involvement with academic research means we’re well-equipped to know about the latest, most effective arthritis treatments.
WMCHealth offers a convenient on-site infusion center for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis who need DMARD infusions.